EFFECTS OF AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES ON MUSCLES AND LIGAMENTS

DR VAIJAYANTI LAGU-JOSHI
CONSULTANT RHEUMATOLOGIST
Rheumatic diseases are diverse, multifactorial diseases. Rheumatic diseases affect not only joints but also affect muscles, bones and periarticular tissues like tendons, ligaments, connective tissue. Some of them are autoimmune in nature caused due to altered immune responses against self-tissues for example: Rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, inflammatory myositis.

There are three main types of muscles: skeletal muscles, in upper and lower limbs that can be voluntarily controlled, smooth muscles that are involuntary, control breathing, and digestion; involuntary cardiac muscles, which control the function of the heart. Skeletal muscles travel across the length of joints and stretch between the bones. All muscles in the body contract or shorten when they receive nerve signals initiated by the brain.
Ligaments and tendons are fibrous bands of connective tissue that attach to bone. Ligaments connect two or more bones together and help stabilize joints. Since they have limited stretching ability, they limit how far a joint moves to help protect against injury.
Tendons attach muscle to bone. Tendons vary in size and are somewhat elastic and connect muscles to bones. Their job is to transmit force between the bones and the muscle.
Major tendons in body are Achilles tendon at the heel, rotator cuff in shoulder.
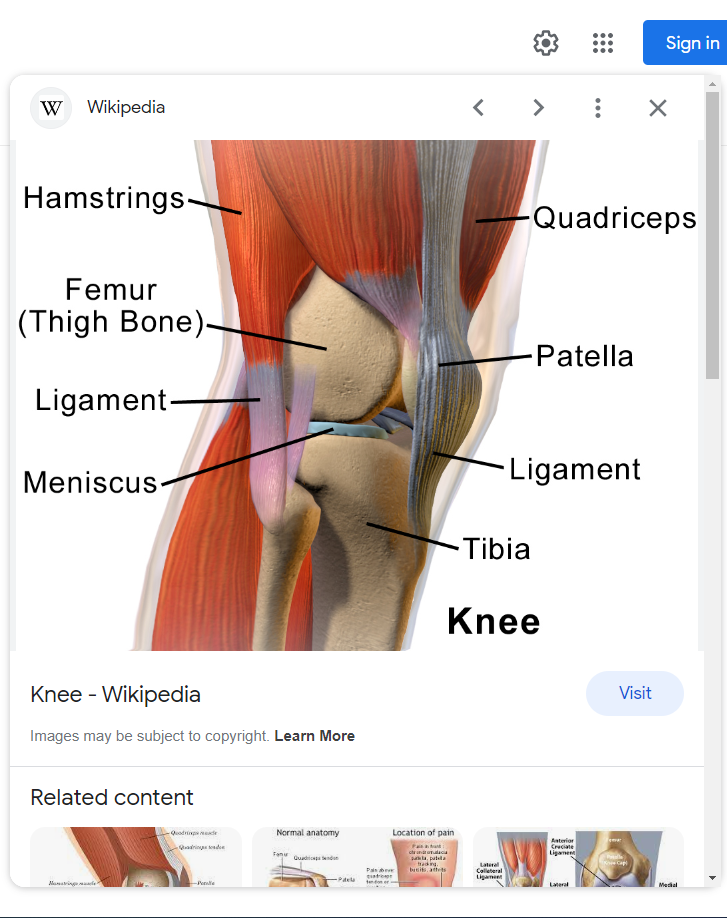
Here is a schematic diagram of knee joint and periarticular structures.
Tendinosis/ tendinitis:
Tendonitis is inflammation of tendons. It usually develops when these tendons are overused, injured or if there is a pre-existing rheumatic condition. The Achilles tendon is a large tendon that connects calf muscles to the bony calcaneum.
Psoriatic arthritis is an important cause of tendinitis especially at heel. Long standing rheumatoid arthritis can also cause periarticular tendinitis in knees, shoulders, wrists and hands. Seronegative spondylo-arthropathies can cause inflammation of tendons around hip and heel.
Symptoms usually include pain, tenderness and restricted movement of the joints.
Tendinitis / tenosynovitis can be picked up on ultrasound.
Tendon tear:
Long standing inflammation in tendons can lead to tears. Rheumatoid arthritis can cause such tears in extensors of fingers of hands. It becomes difficult to lift up the finger then and that affects the daily functioning
A rotator cuff tear is a rip in the group of four muscles and tendons that stabilize shoulder joint.

Rotator cuff injuries of shoulder are most often caused by progressive wear and tear of the tendon tissue over time. Repetitive overhead activity or prolonged bouts of heavy lifting can irritate or damage the tendon. The rotator cuff can also be injured in a single incident during falls or accidents.
The tears are diagnosed by ULTRASOUND / MRI techniques.
LIGAMENT INVOLVEMENT:
Inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis cause synovitis and affect tendons and ligaments too. Weakened ligaments can cause joint deformities - such as claw toe or hammer toe, hand deformities of RA.
MYALGIA:
Myalgia is diffuse muscle pains. Viral infections like Chikungunya, dengue fever can present as myalgias and arthralgia. They generally settle with symptomatic measures and rest.
Fibromyalgia - a chronic condition in young females .There is diffuse pain all over body, sleep problems, fatigue, and often emotional and mental distress. Exercise, positive mindset, stress relaxation are mainstay in treatment of fibromyalgia.
MYOSITIS:
The idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) are the inflammatory muscle diseases. They are a heterogeneous group of autoimmune inflammatory muscle conditions comprising mainly of dermatomyositis and polymyositis. They present with muscle weakness, myalgia, swallowing and breathing difficulties in some. In dermatomyositis there are skin rashes as well.
The diagnosis is made by raised muscle enzymes, abnormal electromyography (EMG), abnormal muscle biopsies and myositis-related antibodies.
Inflammatory myositis are treated with steroids and immunosuppresants and physiotherapy helps to strengthen muscles
Overlap/ mixed connective tissue diseases, lupus can also show myositis.
MYOPATHY :
In myopathy there is muscle weakness and pain but there may not be any inflammation. Patients with Rheumatoid arthritis can have lower muscle mass and weakness secondary to active joint pain and swellings or deformities of joints. Deformities and active disease lead to impaired physical function and a greater tendency toward physical inactivity.
Osteoarthritis of knees is a degenerative arthritis which can also show muscle weakness due to sarcopenia and inactivity due to pain.
Sometimes medications used in treating a number of rheumatic disease can show myopathy. Glucocorticoids are powerful anti-inflammatory agents and have a variety of uses in rheumatology. Steroid induced myopathy is a known side effect of steroids that needs to be differentiated from active myositis.
Various autoimmune diseases can affect muscles and periarticular structures apart from arthritis, thus correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment are needed. Sometimes the treatment is with medication, sometimes with physiotherapy alone or in combination with medications and sometimes surgical repair is necessary to tackle tendon /ligament ruptures








